首先,文末加了一个稳定性的问答彩蛋。毕竟这个“完整版”版本是我自用的。
其次,23问完整版的很多观点我在 图说质控---第二期( 图说质控---第二期) 第一课(
图说质控---第二期) 第一课( 第一课) 和 第八课(
第一课) 和 第八课( 第八课) 都有些结合实例的介绍,为啥没人发现呢?
第八课) 都有些结合实例的介绍,为啥没人发现呢?
最后,发出这个回锅肉是为了凑齐。具体见前文: 接着扒:欧盟 附录11 计算机化系统 官方补充要求( 接着扒:欧盟 附录11 计算机化系统 官方补充要求)
接着扒:欧盟 附录11 计算机化系统 官方补充要求)
最最后,10664字,这是我发的单篇最长的,有点长,你忍忍(但小库说是32082个字)。
Data integrity (New August 2016)
Data integrity
Data integrity enables good decision-making by pharmaceutical manufacturers and regulatory authorities.It is a fundamental requirement of the pharmaceutical quality system described in EU GMP chapter 1, applying equally to manual (paper) and electronic systems.
数据完整性使制药商和监管机构能够做出良好的决策。这是欧盟GMP第1章中描述的药品质量体系的基本要求,同样适用于手动(纸质)和电子系统。
Promotion of a quality culture together with implementation of organisational and technical measures which ensure data integrity is the responsibility of senior management. It requires participation and commitment by staff at all levels within the company, by the company's suppliers and by its distributors.
促进质量文化以及实施确保数据完整性的组织和技术措施是高级管理层的责任。它需要公司内各级员工、公司供应商和分销商的参与和承诺。
Senior management should ensure that data integrity risk is assessed, mitigated and communicated in accordance with the principles of quality risk management. The effort and resource assigned to data integrity measures should be commensurate with the risk to product quality, and balanced with other quality assurance resource demands. Where long term measures are identified in order to achieve the desired state of control, interim measures should be implemented to mitigate risk, and should be monitored for effectiveness.
高级管理层应确保根据质量风险管理原则评估、减轻和传达数据完整性风险。分配给数据完整性措施的努力和资源应与产品质量风险相称,并与其他质量保证资源需求相平衡。在确定长期措施以达到理想的控制状态时,应采取临时措施以减轻风险,并应监测其有效性。
The following questions and answers describe foundational principles which facilitate successful implementation of existing guidance published by regulatory authorities participating in the PIC/S scheme. It should be read in conjunction with national guidance, medicines legislation and the GMP standards published in Eudralex volume 4.
以下问题和答案描述了有助于成功实施参与PIC/S计划的监管机构发布的现有指南的基本原则。它应与国家指南,药品立法和欧盟法规第4卷中发布的GMP标准一起阅读。
The importance of data integrity to quality assurance and public health protection should be included in personnel training programmes.
数据完整性对质量保证和公共卫生保护的重要性应纳入人员培训方案。
•WHO - Annex 5: guidance on good data and record management practices
•世卫组织 - 附件5:关于良好数据和记录管理做法的指导
1. How can data risk be assessed? 如何评估数据风险?
Data risk assessment should consider the vulnerability of data to involuntary or deliberate amendment, deletion or recreation. Control measures which prevent unauthorised activity and increase visibility / detectability can be used as risk mitigating actions.
数据风险评估应考虑数据在非自愿或故意修改、删除或重新创建中的脆弱性。防止未经授权的活动和提高可见性/可检测性的控制措施可用作风险缓解措施。
Examples of factors which can increase risk of data integrity failure include complex, inconsistent processes with open-ended and subjective outcomes. Simple tasks which are consistent, well-defined and objective lead to reduced risk.
可能增加数据完整性故障风险的因素示例包括具有开放式和主观结果的复杂、不一致的流程。一致、明确和客观的简单任务可以降低风险。
Risk assessment should include a business process focus (e.g. production, QC) and not just consider IT system functionality or complexity. Factors to consider include:
风险评估应包括业务流程重点(例如生产,质量控制),而不仅仅是考虑IT系统的功能或复杂性。需要考虑的因素包括:
•Process complexity流程复杂性
•Process consistency, degree of automation /human interface流程一致性、自动化程度/人机界面
•Subjectivity of outcome / result输出/结果的主观性
•Is the process open-ended or well defined流程是开放式的还是定义明确的
This ensures that manual interfaces with IT systems are considered in the risk assessment process. Computerised system validation in isolation may not result in low data integrity risk, in particular when the user is able to influence the reporting of data from the validated system.
这可确保在风险评估过程中考虑与IT系统的手动接口。单独的计算机化系统验证可能不会降低数据完整性风险,特别是当用户能够影响来自已验证系统的数据报告时。
2. How can data criticality be assessed? 如何评估数据关键性?
The decision which data influences may differ in importance, and the impact of the data to a decision may also vary. Points to consider regarding data criticality include:
数据影响哪些决策的重要性可能不同,数据对决策的影响也可能不同。有关数据关键性需要考虑的要点包括:
•What decision does the data influence? 数据会影响什么决策?
For example: when making a batch release decision, data which determines compliance with critical quality attributes is of greater importance than warehouse cleaning records.
例如:在做出批次放行决策时,确定是否符合关键质量属性的数据比仓库清洁记录更重要。
•What is the impact of the data to product quality or safety? 数据对产品质量或安全有什么影响?
For example: for an oral tablet, active substance assay data is of greater impact to product quality and safety than tablet dimensions' data. 例如:对于口服片剂,活性物质检测数据对产品质量和安全性的影响大于片剂尺寸数据。
3. What does 'Data Lifecycle' refer to? “数据生命周期”指的是什么?
'Data lifecycle' refers to how data is generated, processed, reported, checked, used for decision-making, stored and finally discarded at the end of the retention period.
“数据生命周期”是指数据如何生成、处理、报告、检查、用于决策、存储和最终在保留期结束时丢弃。
Data relating to a product or process may cross various boundaries within the lifecycle, for example: 与产品或过程相关的数据可能跨越生命周期中的各种界限,例如:
•IT systems信息技术系统
oQuality system applications质量体系应用
oProduction生产
oAnalytical分析
oStock management systems库存管理系统
oData storage (back-up and archival) 数据存储(备份和存档)
•Organisational组织
oInternal (e.g. between production, QC and QA) 内部(例如,在生产、质量控制和质量保证之间)
oExternal (e.g. between contract givers and acceptors) 外部(例如合同给予者和接受者之间)
oCloud-based applications and storage基于云的应用程序和存储
4. Why is 'Data lifecycle' management important to ensure effective data integrity measures?
为什么“数据生命周期”管理对于确保有效的数据完整性措施很重要?
Data integrity can be affected at any stage in the lifecycle. It is therefore important to understand the lifecycle elements for each type of data or record, and ensure controls which are proportionate to data criticality and risk at all stages.
数据完整性在生命周期的任何阶段都可能受到影响。因此,了解每种类型的数据或记录的生命周期元素,并确保在所有阶段进行与数据关键性和风险成比例的控制非常重要。
5. What should be considered when reviewing the 'Data lifecycle'? 在审查“数据生命周期”时应考虑什么?
The 'Data lifecycle' refers to the:
“数据生命周期”是指:
•Generation and recording of data数据的生成和记录
•Processing into usable information处理成可用信息
•Checking the completeness and accuracy of reported data and processed information检查报告数据和处理信息的完整性和准确性
•Data (or results) are used to make a decision数据(或结果)用于做出决策
•Retaining and retrieval of data which protects it from loss or unauthorised amendment保留和检索数据,防止数据丢失或未经授权的修改
•Retiring or disposal of data in a controlled manner at the end of its life在数据生命周期结束时以受控方式停用或处置数据
'Data Lifecycle' reviews are applicable to both paper and electronic records, although control measures may be applied differently. In the case of computerised systems, the 'data lifecycle' review should be performed by business process owners (e.g. production, QC) in collaboration with IT personnel who understand the system architecture. The description of computerised systems required by EU GMP Annex 11 paragraph 4.3 can assist this review. The application of critical thinking skills is important to not only identify gaps in data governance, but to also challenge the effectiveness of the procedural and systematic controls in place.
“数据生命周期”审查适用于纸质和电子记录,尽管控制措施的应用可能有所不同。对于计算机化系统,“数据生命周期”审查应由业务流程所有者(例如生产,QC)与了解系统架构的IT人员合作执行。欧盟GMP附录11第4.3段要求的计算机化系统的描述可以帮助进行此审查。批判性思维技能的应用不仅对于识别数据治理中的差距很重要,而且对于挑战现有程序和系统控制的有效性也很重要。
Segregation of duties between data lifecycle stages provides safeguards against data integrity failure by reducing the opportunity for an individual to alter, misrepresent or falsify data without detection.
数据生命周期阶段之间的职责分离通过减少个人在不被发现的情况下更改、歪曲或伪造数据的机会,提供了防止数据完整性故障的保障。
Data risk should be considered at each stage of the data lifecycle review.
在数据生命周期审核的每个阶段都应考虑数据风险。
6. 'Data lifecycle': What risks should be considered when assessing the generating and recording of data?
“数据生命周期”:在评估数据的生成和记录时应考虑哪些风险?
The following aspects should be considered when determining risk and control measures:
在确定风险和控制措施时,应考虑以下几个方面:
•How and where is original data created (i.e. paper or electronic) 原始数据创建方式和地点(即纸质或电子)
•What metadata is associated with the data, to ensure a complete, accurate and traceable record, taking into account ALCOA principles. Does the record permit the reconstruction of the activity哪些元数据与数据相关联,以确保完整、准确和可追溯的记录,同时考虑到 ALCOA 原则。记录是否允许重建活动
•Where is the data and metadata located数据和元数据位于何处
•Does the system require that data is saved to permanent memory at the time of recording, or is it held in a temporary buffer系统是否要求在记录时将数据保存到永久存储器中,还是保存在临时缓冲区中
In the case of some computerised analytical and manufacturing equipment, data may be stored as a temporary local file prior to transfer to a permanent storage location (e.g. server). During the period of 'temporary' storage, there is often limited audit trail provision amending, deleting or recreating data. This is a data integrity risk. Removing the use of temporary memory (or reducing the time period that data is stored in temporary memory) reduces the risk of undetected data manipulation.
对于某些计算机化的分析和制造设备,数据可能会在传输到永久存储位置(例如服务器)之前作为临时本地文件存储。在“临时”存储期间,修改、删除或重新创建数据的审计跟踪规定通常有限。这是数据完整性风险。删除缓存的使用(或减少数据存储在缓存中的时间段)可降低未检测到的数据操作的风险。
•Is it possible to recreate, amend or delete original data and metadata; 是否可以重新创建、修改或删除原始数据和元数据;
Controls over paper records are discussed elsewhere in this guidance. 对纸质记录的控制将在本指南的其他部分讨论。
Computerised system controls may be more complex, including setting of user privileges and system configuration to limit or prevent access to amend data. It is important to review all data access opportunities, including IT helpdesk staff, who may make changes at the request of the data user. These changes should be procedurally controlled, visible and approved within the quality system.
计算机化的系统控制可能更复杂,包括设置用户权限和系统配置以限制或阻止访问修改数据。请务必查看所有数据访问机会,包括 IT 帮助台人员,他们可能会根据数据用户的请求进行更改。这些变化应在质量体系内进行程序控制、可见和批准。
•How data is transferred to other locations or systems for processing or storage; 如何将数据传输到其他位置或系统进行处理或存储;
Data should be protected from possibility of intentional or unintentional loss or amendment during transfer to other systems (e.g. for processing, review or storage). Paper records should be protected from amendment, or substitution. Electronic interfaces should be validated to demonstrate security and no corruption of data, particularly where systems require an interface to present data in a different structure or file format.
应保护数据在传输到其他系统(例如处理、审查或存储)期间避免有意或无意丢失或修改的可能性。应保护纸质记录不被修改或替换。应验证电子接口以证明安全性和数据没有损坏,特别是当系统需要接口以不同的结构或文件格式呈现数据时。
Does the person processing the data have the ability to influence what data is reported, or how it is presented.
处理数据的人员是否有能力影响报告哪些数据或呈现方式?
7. 'Data lifecycle': What risks should be considered when assessing the processing data into usable information?
“数据生命周期”:在评估将数据处理为可用信息时应考虑哪些风险?
The following aspects should be considered when determining risk and control measures:
在确定风险和控制措施时,应考虑以下几个方面
•How is data processed; 如何处理数据;
Data processing methods should be approved, identifiable and version controlled. In the case of electronic data processing, methods should be locked where appropriate to prevent unauthorised amendment.
数据处理方法应获得批准、可识别和版本控制。在电子数据处理的情况下,应酌情锁定方法,以防止未经授权的修改。
•How is data processing recorded; 如何记录数据处理;
The processing method should be recorded. In situations where raw data has been processed more than once, each iteration (including method and result) should be available to the data checker for verification.
应记录处理方法。在原始数据被多次处理的情况下,每个迭代(包括方法和结果)都应可供数据检查器进行验证。
•Does the person processing the data have the ability to influence what data is reported, or how it is presented; 处理数据的人员是否有能力影响报告哪些数据或呈现方式;
Even 'validated systems' which do not permit the user to make any changes to data may be at risk if the user can choose what data is printed, reported or transferred for processing. This includes performing the activity multiple times as separate events and reporting a desired outcome from one of these repeats.
如果用户可以选择打印、报告或传输哪些数据进行处理,即使是不允许用户对数据进行任何更改的“经过验证的系统”也可能面临风险。这包括将活动作为单独的事件多次执行,并报告其中一个重复的所需结果。
Data presentation (e.g. changing scale of graphical reports to enhance or reduce presentation of analytical peaks) can also influence decision making, and therefore impact data integrity.
数据呈现(例如,改变图形报告的规模以增强或减少分析峰的呈现)也会影响决策,从而影响数据完整性。
8. 'Data lifecycle': What risks should be considered when checking the completeness and accuracy of reported data and processed information?
“数据生命周期”:在检查报告数据和处理信息的完整性和准确性时应考虑哪些风险?
The following aspects should be considered when determining risk and control measures:
在确定风险和控制措施时,应考虑以下几个方面:
•Is original data (including the original data format) available for checking; 原始数据(包括原始数据格式)是否可供核对;
The format of the original data (electronic or paper) should be preserved, and available to the data reviewer in a manner which permits interaction with the data (e.g. search, query). This approach facilitates a risk-based review of the record, and can also reduce administrative burden for instance utilising validated audit trail 'exception reports' instead of an onerous line-by-line review.
原始数据(电子或纸质)的格式应予保留,并以允许与数据交互的方式提供给数据审查员(例如搜索、查询)。这种方法有助于对记录进行基于风险的审查,还可以减轻管理负担,例如使用经过验证的审计跟踪“异常报告”,而不是繁琐的逐行审查。
•Are there any periods of time when data is not audit trailed; 是否有任何时间段的数据未被审计跟踪;
This may present opportunity for data amendment which is not subsequently visible to the data reviewer. Additional control measures should be implemented to reduce risk of undisclosed data manipulation.
这可能会为数据修改提供机会,而数据审查者随后看不到这些机会。应实施额外的控制措施,以减少未披露数据操纵的风险。
•Does the data reviewer have visibility and access to all data generated; 数据审阅者是否能够查看和访问生成的所有数据;
This should include any data from failed or aborted activities, discrepant or unusual data which has been excluded from processing or the final decision-making process. Visibility of all data provides protection against selective data reporting or 'testing into compliance'.
这应包括来自失败或中止活动的任何数据,已从处理或最终决策过程中排除的差异或异常数据。所有数据的可见性可防止选择性数据报告或“合规性测试”。
•Does the data reviewer have visibility and access to all processing of data; 数据审查员是否能够查看和访问所有数据处理;
This ensures that the final result obtained from raw data is based on good science, and that any data exclusion or changes to processing method is based on good science. Visibility of all processing information provides protection against undisclosed 'processing into compliance'.
这确保了从原始数据中获得的最终结果是基于良好的科学原则,并且任何数据排除或对处理方法的更改都是基于良好的科学原则。所有处理信息的可见性可防止未公开的“处理为法规遵从性”。
9. 'Data lifecycle': What risks should be considered when data (or results) are used to make a decision?
“数据生命周期”:使用数据(或结果)做出决策时应考虑哪些风险?
The following aspects should be considered when determining risk and control measures:
在确定风险和控制措施时,应考虑以下几个方面:
•When is the pass / fail decision taken; 何时做出通过/失败决定;
If data acceptability decisions are taken before a record (raw data or processed result) is saved to permanent memory, there may be opportunity for the user to manipulate data to provide a satisfactory result, without this change being visible in audit trail. This would not be visible to the data reviewer.
如果在将记录(原始数据或处理后的结果)保存到永久内存之前做出数据可接受性决策,则用户可能有机会操作数据以提供令人满意的结果,而此更改在审计跟踪中不可见。这对数据审阅者是不可见的。
This is a particular consideration where computerised systems alert the user to an out of specification entry before the data entry process is complete (i.e. the user 'saves' the data entry), or saves the record in temporary memory.
当计算机化系统在数据输入过程完成之前提醒用户不合规格的输入(即用户“保存”数据输入)或将记录保存在缓存中时,这是一个特别的考虑因素。
10. 'Data lifecycle': What risks should be considered when retaining and retrieving data to protect it from loss or unauthorised amendment?
“数据生命周期”:在保留和检索数据以防止数据丢失或未经授权的修改时应考虑哪些风险?
The following aspects should be considered when determining risk and control measures:
在确定风险和控制措施时,应考虑以下几个方面:
•How / where is data stored; 数据存储方式/位置;
Storage of data (paper or electronic) should be at secure locations, with access limited to authorised persons. The storage location must provide adequate protection from damage due to water, fire, etc.
数据(纸质或电子)的存储应位于安全的位置,仅限授权人员访问。存储位置必须提供足够的保护,防止因水、火等造成的损坏。
•What are the measures protecting against loss or unauthorised amendment; 有哪些措施防止丢失或未经授权的修改;
Data security measures should be at least equivalent to those applied during the earlier Data lifecycle stages. Retrospective data amendment (e.g. via IT helpdesk or data base amendments) should be controlled by the pharmaceutical quality system, with appropriate segregation of duties and approval processes.
数据安全措施应至少与早期数据生命周期阶段应用的措施相当。追溯性数据修订(例如通过IT服务台或数据库修订)应由药品质量体系控制,并适当划分职责和审批流程。
•Is data backed up in a manner permitting reconstruction of the activity; 数据备份的方式是否允许重建活动;
Back-up arrangements should be validated to demonstrate the ability to restore data following IT system failure. In situations where metadata (including relevant operating system event logs) are stored in different file locations from raw data, the back-up process should be carefully designed to ensure that all data required to reconstruct a record is included.
应验证备份安排,以证明在 IT 系统故障后恢复数据的能力。在元数据(包括相关的操作系统事件日志)与原始数据存储在不同的文件位置的情况下,应仔细设计备份过程,以确保包括重建记录所需的所有数据。
Similarly, 'true copies' of paper records may be duplicated on paper, microfilm, or electronically, and stored in a separate location.
同样,纸质记录的“真实副本”可以复制在纸张、缩微胶卷或电子上,并存储在单独的位置。
•What are ownership / retrieval arrangements, particularly considering outsourced activities or data storage; 什么是所有权/检索安排,特别是考虑到外包活动或数据存储;
A technical agreement should be in place which addresses the requirements of Part I Chapter 7 and Part II Section 16 of the GMP guide.
应制定技术协议,解决GMP指南第一部分第7章和第二部分第16节的要求。
11. 'Data lifecycle': What risks should be considered when retiring or disposal of data in a controlled manner at the end of its life?
“数据生命周期”:在数据生命周期结束时以受控方式停用或处置数据时应考虑哪些风险?
The following aspects should be considered when determining risk and control measures:
在确定风险和控制措施时,应考虑以下几个方面:
•The data retention period数据保留期
This will be influenced by regulatory requirements and data criticality. When considering data for a single product, there may be different data retention needs for pivotal trial data and manufacturing process / analytical validation data compared to routine commercial batch data.
这将受到法规要求和数据关键性的影响。在考虑单个产品的数据时,与常规的商业批次数据相比,关键试验数据和制造过程/分析验证数据的数据保留需求可能不同。
•How data disposal is authorised如何授权数据处理
Any disposal of data should be approved within the quality system and be performed in accordance with a procedure to ensure compliance with the required data retention period.
任何数据处理都应在质量体系内获得批准,并按照确保符合所需数据保留期的程序进行。
12. Is it required by the EU GMP to implement a specific procedure for data integrity?
欧盟GMP是否要求实施数据完整性的特定程序?
There is no requirement for a specific procedure, however it may be beneficial to provide a summary document which outlines the organisations total approach to data governance. 不需要特定的程序,但是提供一份概述组织数据治理总体方法的摘要文件可能是有益的。
A compliant pharmaceutical quality system generates and assesses a significant amount of data. While all data has an overall influence on GMP compliance, different data will have different levels of impact to product quality.
合规的药品质量体系会生成和评估大量数据。虽然所有数据都对GMP合规性有总体影响,但不同的数据会对产品质量产生不同程度的影响。
A quality-risk management (ICH Q9) approach to data integrity can be achieved by considering data risk and data criticality at each stage in the Data lifecycle. The effort applied to control measures should be commensurate with this data risk and criticality assessment.
通过在数据生命周期的每个阶段考虑数据风险和数据关键性,可以实现数据完整性的质量风险管理方法(ICHQ9)。用于控制措施的努力应与这种数据风险和关键性评估相称。
The approach to risk identification, mitigation, review and communication should be iterative, and integrated into the pharmaceutical quality system. This should provide senior management supervision and permit a balance between data integrity and general GMP priorities in line with the principles of ICH Q9 & Q10.
风险识别、缓解、审查和沟通的方法应该是迭代的,并整合到药品质量体系中。这应该提供高级管理层监督,并根据ICH Q9和Q10的原则在数据完整性和一般GMP优先级之间取得平衡。
13. How are the data integrity expectations (ALCOA) for the pharmaceutical industry prescribed in the existing EU GMP relating to active substances and dosage forms published in Eudralex volume 4?
现有欧盟GMP中对法规第4卷中公布的活性物质和剂型相关的制药行业数据完整性期望(ALCOA)是如何规定的?
The main regulatory expectation for data integrity is to comply with the requirement of ALCOA principles. The table below provide for each ALCOA principle the link to EU GMP
对数据完整性的主要监管期望是遵守ALCOA原则的要求。下表提供了ALCOA原则与欧盟GMP参考的链接(第一部分,第二部分和附件11):
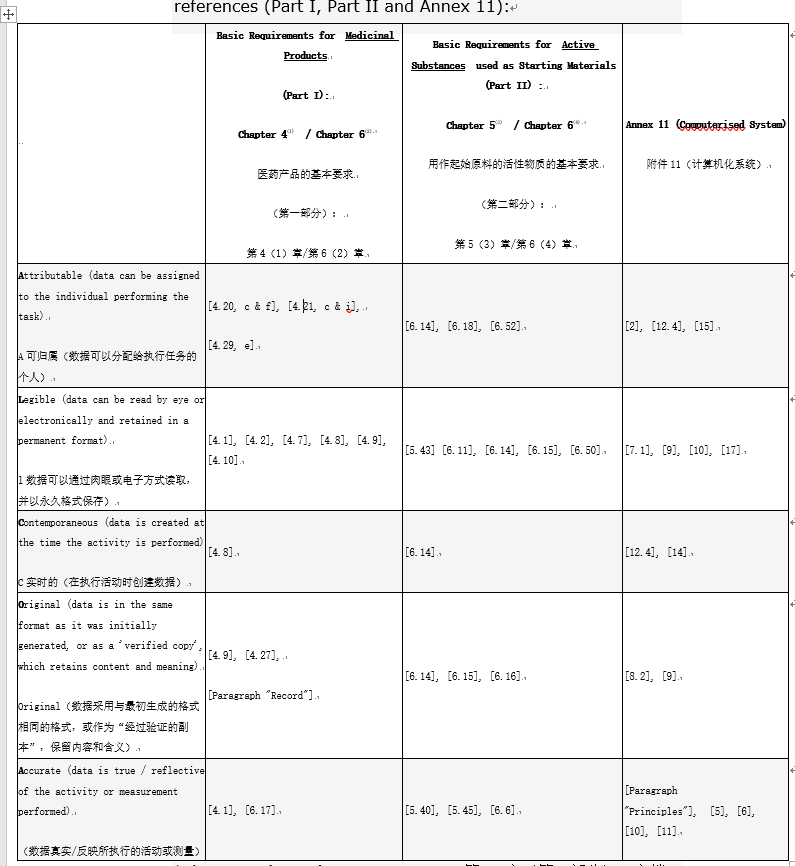
1Chapter 4 (Part I): Documentation第 4 章(第一部分):文档
2Chapter 6 (Part I): Quality control第6章(第一部分):质量控制
3Chapter 5 (Part II): Process equipment (computerized system) 第5章(第二部分):工艺设备(计算机化系统)
4Chapter 6 (Part II): Documentation and records第6章(第二部分):文件和记录
14. How should the company design and control their paper documentation system to prevent the unauthorised re-creation of GMP data?
公司应如何设计和控制其纸质文档系统,以防止未经授权重新创建GMP数据?
The template (blank) forms used for manual recordings may be created in an electronic system (Word, Excel, etc.). The corresponding master documents should be approved and controlled electronically or in paper versions. The following expectations should be considered for the template (blank) form:
用于手动记录的模板(空白)表格可以在电子系统(Word,Excel等)中创建。相应的主文件应以电子或纸质版本进行批准和控制。对于模板(空白)表单,应考虑以下期望:
•have a unique reference number (including version number) and include reference to corresponding SOP number具有唯一的参考编号(包括版本号),并包括对相应SOP编号的引用
•should be stored in a manner which ensures appropriate version control应以确保适当的版本控制的方式存储
•if signed electronically, should use a secure e-signature如果以电子方式签名,则应使用安全的电子签名
The distribution of template records (e.g. 'blank' forms) should be controlled. The following expectations should be considered where appropriate, based on data risk and criticality: 应控制模板记录(例如“空白”表单)的分发。根据数据风险和关键性,应酌情考虑以下预期:
•enable traceability for issuance of the blank form by using a bound logbook with numbered pages or other appropriate system. For loose leaf template forms, the distribution date, a sequential issuing number, the number of the copies distributed, the department name where the blank forms are distributed, etc. should be known通过使用带有编号页的装订日志或其他适当的系统,启用空白表单签发的可追溯性。对于活页模板表格,应知道分发日期、顺序发行编号、分发副本的数量、分发空白表单的部门名称等。
•Distributed copies should be designed to avoid photocoping either by using a secure stamp, or by the use of paper colour code not available in the working areas or another appropriate system. 分发副本的设计应避免影印,使用安全印章,或使用工作区或其他适当系统中没有的纸质颜色代码。
15. What controls should be in place to ensure original electronic data is preserved?
应采取哪些控制措施来确保原始电子数据得到保存?
Computerised systems should be designed in a way that ensures compliance with the principles of data integrity. The system design should make provisions such that original data cannot be deleted and for the retention of audit trails reflecting changes made to original data.
计算机化系统的设计应确保符合数据完整性原则。系统设计应作出规定,使原始数据不能被删除,并保留反映对原始数据所做的更改的审计线索。
16. Why is it important to review electronic data?
为什么审查电子数据很重要?
In the case of data generated from an electronic system, electronic data is the original record which must be reviewed and evaluated prior to making batch release decisions and other decisions relating to GMP related activities (e.g. approval of stability results, analytical method validation etc.). In the event that the review is based solely on printouts there is potential for records to be excluded from the review process which may contain un-investigated out of specification data or other data anomalies. The review of the raw electronic data should mitigate risk and enable detection of data deletion, amendment, duplication, reusing and fabrication which are common data integrity failures.
对于从电子系统生成的数据,电子数据是原始记录,在做出批次放行决定和与GMP相关活动相关的其他决定(例如批准稳定性结果,分析方法验证等)之前,必须对其进行审查和评估。如果审查仅基于打印输出,则记录可能会被排除在审查过程之外,其中可能包含未经调查的不合格数据或其他数据异常。对原始电子数据的审查应降低风险,并能够检测数据删除、修改、复制、重复使用和捏造,这些都是常见的数据完整性故障。
Example of an inspection citing: 引用的检查示例:
Raw data for HPLC/GC runs which had been invalidated was stored separately to the QC raw data packages and had not been included in the review process. 无效的HPLC/GC运行的原始数据被单独存储在QC原始数据包中,未包含在审查过程中。
In the above situation, the procedure for review of chromatographic data packages did not require a review of the electronic raw data or a review of relevant audit trails associated with the analyses. This lead to the exclusion of records from the review process and to lack of visibility of changes made during the processing and reporting of the data. The company was unable to provide any explanation for the data which had been invalidated.
在上述情况下,审查色谱数据包的程序不需要审查电子原始数据或审查与分析相关的审计线索。这导致将记录排除在审查过程之外,并导致无法看到在处理和报告数据期间所做的更改。该公司无法对无效的数据提供任何解释。
17. Is a risk-based review of electronic data acceptable?
是否可以接受基于风险的电子数据审查?
Yes. The principles of quality risk management may be applied during the review of electronic data and review by exception is permitted, when scientifically justified.
是的。在审查电子数据期间可以适用质量风险管理原则,在科学上合理的情况下,允许例外审查(引申查证?)。
Exception Reporting is used commonly as a tool to focus the review of electronic data such as (but not limited to) electronic batch records. Exception reporting rapidly highlights to the reviewer one of the most critical elements of batch review, i.e. the exceptions. The level of review of the full electronic batch record can vary based on the exceptions as well as the level of confidence and experience with a particular process. Appropriate testing and validation must be completed for the automated system and the output Batch Exception Report to ensure its functionality meets the business and regulatory requirements as per GMP.
异常报告通常用作集中审查电子数据(例如(但不限于)电子批次记录)的工具。异常报告可以快速向审核员突出显示批次审核中最关键的要素之一,即异常。完整电子批次记录的审查级别可能因例外情况以及对特定过程的信心和经验水平而异。必须对自动化系统和输出批次异常报告完成适当的测试和验证,以确保其功能符合GMP的业务和法规要求。
18. What are the expectations for the self-inspection program related to data integrity?
对与数据完整性相关的自检计划有什么期望?
Ongoing compliance with the company's data governance policy/procedures should be reviewed during self-inspection, to ensure that they remain effective. This may also include elements of the Data lifecycle discussed in Q3-Q9.
在自检期间,应审查对公司数据治理政策/程序的持续遵守情况,以确保其保持有效。这可能还包括 Q3-Q9 中讨论的数据生命周期的元素。
19. What are my company's responsibilities relating to data integrity for GMP activities contracted out to another company?
我公司对外包给另一家公司的GMP活动的数据完整性有何责任?
Data integrity requirements should be incorporated into the company's contractor/vendor qualification/assurance program and associated procedures. 数据完整性要求应纳入公司的承包商/供应商资格/保证计划和相关程序
In addition to having their own data governance systems, companies outsourcing activities should verify the adequacy of comparable systems at the contract acceptor. The contract acceptor should apply equivalent levels of control to those applied by the contract giver.
除了拥有自己的数据治理系统外,外包活动的公司还应在合同接受者处验证可比系统的充分性。合同接受人应采用与合同给予者同等的控制水平。
Formal assessment of the contract acceptors competency and compliance in this regard should be conducted in the first instance prior to the approval of a contractor, and thereafter verified on a periodic basis at an appropriate frequency based on risk.
对合同承兑人的能力和遵守情况的正式评估应首先在承包商批准之前进行,然后根据风险以适当的频率定期进行核实。
20. How can a recipient (contract giver) build confidence in the validity of documents such as Certificate of Analysis (CoA) provided by a supplier (contract acceptor)?
收货方(合同给予者)如何建立对供应商(合同接受者)提供的分析证书(CoA)等文件有效性的信心?
The recipient should have knowledge of the systems and procedures implemented at the supplier for the generation of the CoA. Arrangements should be in place to ensure that significant changes to systems are notified and the effectiveness of these arrangements should be subjected to periodic review.
接收方应了解供应商为生成CoA而实施的系统和程序。应作出安排,确保通知系统的重大变化,并定期审查这些安排的有效性。
Data related to activities which are outsourced are routinely provided as summary data in a report format (e.g. CoA). These summary documents are reviewed on a routine basis by the contract acceptor and therefore the review of data integrity at the contract acceptor site on a regular periodic basis (e.g. during on-site audit) takes on even greater significance, in order to build and maintain confidence in the summary data provided.
与外包活动相关的数据通常以报告格式(例如CoA)作为摘要数据提供。这些摘要文件由合同接受者例行审查,因此定期(例如在现场审计期间)在合同接受者现场定期审查数据完整性具有更大的意义,以便建立和保持对所提供的摘要数据的信心。
21. What are the expectations in relation to contract calibration service providers who conduct calibrations on-site and/or off-site? Are audits of these companies premises required?
对于在现场和/或非现场进行校准的合同校准服务提供商的期望是什么?是否需要对这些公司的场所进行审计?
Using the principles of QRM to assess data criticality and risk, the company should include assessment of data governance systems implemented by the service provider when making decisions on service contracts. This may be achieved by on-site audit or desk-based assessment of information submitted by the service provider.
使用QRM的原则来评估数据关键性和风险,公司在做出服务合同决策时应包括对服务提供商实施的数据治理系统的评估。这可以通过对服务提供者提交的信息进行现场审计或文案评估来实现。
22. What is expected of my company in the event that one of my approved contractors is issued with a warning letter/statement of non-compliance concerning data integrity, from a regulatory authority?
如果我的认可承包商之一收到监管机构发出的有关数据完整性的警告信/不合规声明,对我公司的期望是什么?
What is expected of my company in the event that one of my approved contractors (e.g. active substance manufacturer, finished product manufacturer, quality control laboratory etc.) is issued with a warning letter/statement of non-compliance concerning data integrity, from a regulatory authority? 如果我的认可承包商之一(例如活性物质制造商、成品制造商、质量控制实验室等)收到监管机构发出的有关数据完整性的警告信/不合规声明,对我公司的期望是什么?
It is considered that the company should evaluate the risk to its products manufactured/released using the principles of quality risk management. Risk assessments should be made available to Inspectors, on request.
公司应使用质量风险管理原则评估其制造/发布产品的风险。应根据要求向检查专员提供风险评估。
Depending on the outcome of the risk assessment, appropriate action should be taken which may entail delisting the contractor from the approved contractor list. In the event that abnormal disruption in supply may result from a contractor compliance situation, relevant regulatory authorities should be consulted in this regard.
根据风险评估的结果,应采取适当行动,可能需要将承包商从核准的承包商名单上除名。如果承包商合规情况可能导致供应异常中断,则应就此咨询相关监管机构。
23. Where does my company's responsibility begin and end in relation to data integrity aspects of the supply chain for medicinal products?
在医药产品供应链的数据完整性方面,我公司的责任从哪里开始和结束?
All actors in the supply chain play an important part in overall data integrity and assurance of product quality.
供应链中的所有参与者在整体数据完整性和产品质量保证方面都发挥着重要作用。
Data governance systems should be implemented from the manufacture of starting materials right through to the delivery of medicinal products to persons authorised or entitled to supply medicinal products to the public.
数据治理系统应从起始材料的制造一直到向授权或有权向公众供应医药产品的人员交付医药产品。
Relative responsibilities and boundaries should be documented in the contracts between the relevant parties. Final responsibility of ensuring compliance throughout the supply chain rests with batch certifying QP.
相关责任和界限应记录在相关方之间的合同中。确保整个供应链合规性的最终责任在于批量认可QP。
GDP要求(2018年6月新增)---彩蛋
1. Is it acceptable that storage conditions are not monitored for medicinal products which do not have any predefined storage conditions on the outer packaging?
对于外包装上没有任何预定义储存条件的药品,是否可以不监测储存条件?
No. According to the Guideline on declaration of storage conditions (CPMP/QWP/609/96 Rev. 2) , marketing authorisation holders have to provide stability data for storage conditions at 25°C / 60% relative humidity (RH), or 30°C / 65% RH (long term) and 40°C / 75% RH (accelerated), in order to justify not including a statement in the medicinal product labelling.
不。根据 “文档”图标 储存条件声明指南(CPMP/QWP/609/96 Rev. 2) ,上市许可持有人必须提供在 25°C / 60% 相对湿度 (RH) 或 30°C / 65% RH(长期)和 40°C / 75% RH(加速)下储存条件的稳定性数据,以证明不在药品标签中包含声明。
This stability data is generated according to the temperature and humidity conditions of climate zone I (temperate) and II (Mediterranean/subtropical) in Europe. For more information, see the World Health Organization Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations forty-third report, Annex 2: Stability testing of active pharmaceutical ingredients and finished pharmaceutical products.
该稳定性数据是根据欧洲气候区I(温带)和II气候区(地中海/亚热带)的温度和湿度条件生成的。有关更多信息,请参阅 世界卫生组织药物制剂规格专家委员会第四十三次报告,附件2:活性药物成分和成品药物的稳定性测试
No labelling statement means that controls should be in place to maintain conditions relevant to climate zones I and II. Consequently, the temperature should be monitored during storage and transport. Appropriate limits should be set for temperature monitoring to ensure that product stability is not adversely affected.
没有标签声明意味着应采取控制措施,以维持与气候区I和II相关的条件。因此,在储存和运输过程中应监测温度。应为温度监测设置适当的限值,以确保产品稳定性不会受到不利影响。

